Fan Cheng Facebook has developed high-resolution tactile sensors that will improve the efficienc
Published on:2020-07-13
In order to better help human beings complete manual work or tasks, robots must effectively grasp and manipulate surrounding objects. In recent years, although robot researchers have developed more and more technologies to achieve the goal of robot picking and processing objects, most methods are only effective when dealing with very basic tasks, such as picking objects or moving them from one place to another.
High resolution sensors can enable more advanced robot manipulation functions by collecting valuable tactile information, which can be used to identify and manipulate specific objects. Many existing tactile sensors are efficient, but the production cost is expensive, which makes them difficult or impossible to implement on a large scale. Some other products are cheap, but the resolution and performance are limited.
With this in mind, Facebook researchers recently designed digit, a compact, affordable tactile sensor that can also collect high-resolution images. Digit introduced in a pre published paper on arXiv can promote the development of robot, which can complete more tasks involving hand manipulation.
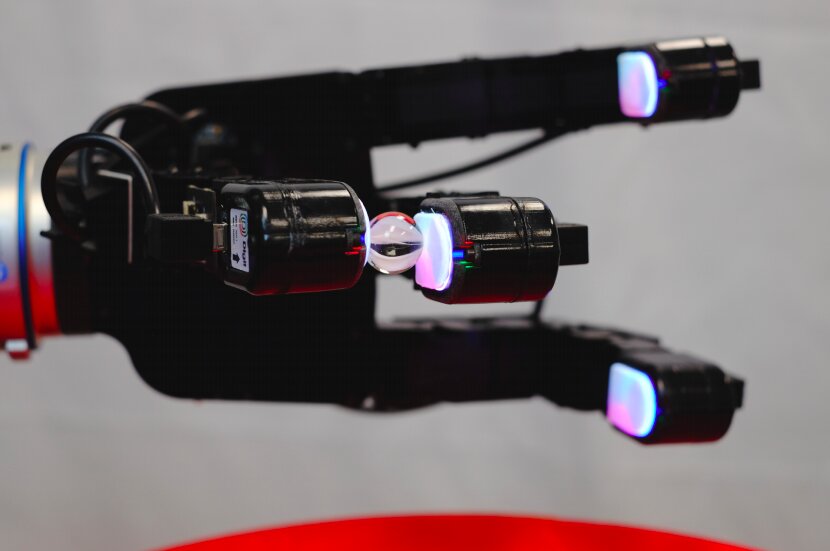
Digit sensors are mounted on Allegro multi fingered hands
"One of the factors limiting the current robot control system is the difficulty of accurately sensing the contact force," the researchers wrote in the paper "Sensing and reasoning about contact forces is essential to accurately control interaction with the environment. As a step towards better robot manipulation, we launched digit, a low-cost, compact and high-resolution tactile sensor suitable for hand manipulation."
The sensor, developed by a team of Facebook researchers, draws inspiration from sensing technologies developed in the past. The newly developed sensors have been miniaturized, so more can be installed on the manipulator.
Digit is a unique and relatively simple design, which makes it easier to mass produce in a short time. Therefore, the sensor is more affordable than other image capture solutions with comparable resolution.
In order to evaluate the performance of digit, researchers applied a sensor on each finger of Allegro hand, a multi fingered robot hand developed by SIMLAB, which is usually used to test the computing technology of object manipulation. In their experiment, they trained a model based on deep neural network to act as the controller of Allegro hand, so that it can manipulate glass marbles. The model is trained using the data collected by digit sensor.
In these tests, the sensor performed well and collected high-resolution tactile data, which can be used to train the deep neural network to guide the Allegro hand to the desired position during the operation task. In the future work, the researchers plan to continue to study their sensors, further reduce their overall dimensions and realize the curved omnidirectional induction field. At the same time, digit sensors can be integrated and tested on various humanoid robots, which potentially enhances their manual operation ability.
High resolution sensors can enable more advanced robot manipulation functions by collecting valuable tactile information, which can be used to identify and manipulate specific objects. Many existing tactile sensors are efficient, but the production cost is expensive, which makes them difficult or impossible to implement on a large scale. Some other products are cheap, but the resolution and performance are limited.
With this in mind, Facebook researchers recently designed digit, a compact, affordable tactile sensor that can also collect high-resolution images. Digit introduced in a pre published paper on arXiv can promote the development of robot, which can complete more tasks involving hand manipulation.

Digit sensors are mounted on Allegro multi fingered hands
"One of the factors limiting the current robot control system is the difficulty of accurately sensing the contact force," the researchers wrote in the paper "Sensing and reasoning about contact forces is essential to accurately control interaction with the environment. As a step towards better robot manipulation, we launched digit, a low-cost, compact and high-resolution tactile sensor suitable for hand manipulation."
The sensor, developed by a team of Facebook researchers, draws inspiration from sensing technologies developed in the past. The newly developed sensors have been miniaturized, so more can be installed on the manipulator.
Digit is a unique and relatively simple design, which makes it easier to mass produce in a short time. Therefore, the sensor is more affordable than other image capture solutions with comparable resolution.
In order to evaluate the performance of digit, researchers applied a sensor on each finger of Allegro hand, a multi fingered robot hand developed by SIMLAB, which is usually used to test the computing technology of object manipulation. In their experiment, they trained a model based on deep neural network to act as the controller of Allegro hand, so that it can manipulate glass marbles. The model is trained using the data collected by digit sensor.
In these tests, the sensor performed well and collected high-resolution tactile data, which can be used to train the deep neural network to guide the Allegro hand to the desired position during the operation task. In the future work, the researchers plan to continue to study their sensors, further reduce their overall dimensions and realize the curved omnidirectional induction field. At the same time, digit sensors can be integrated and tested on various humanoid robots, which potentially enhances their manual operation ability.

