Fan Cheng Secondary driving force of industrial robot: prosperity of high-density robot applicat
Published on:2020-07-03
The demand for industrial robots began with the change of population structure and the rise of labor costs, and flourished in the prominent demand of industrial characteristics. The change of population structure is the result of natural development, followed by the high labor cost, which naturally drives industrial robots to replace artificial labor as a low-cost scheme. After the labor cost and other prominent contradictions between Japan and Germany are basically solved, the growth rate or density of local industrial robots will tend to be flat, but the density increase of industrial robots in South Korea has not slowed down at all and has always maintained a straight-line upward trend, After analysis, we believe that the vigorous development of the downstream application industry of industrial robots is the secondary driving force leading to the prominent demand of industrial robots.
(1) South Korea has the highest density of robots deployed, far exceeding the global average
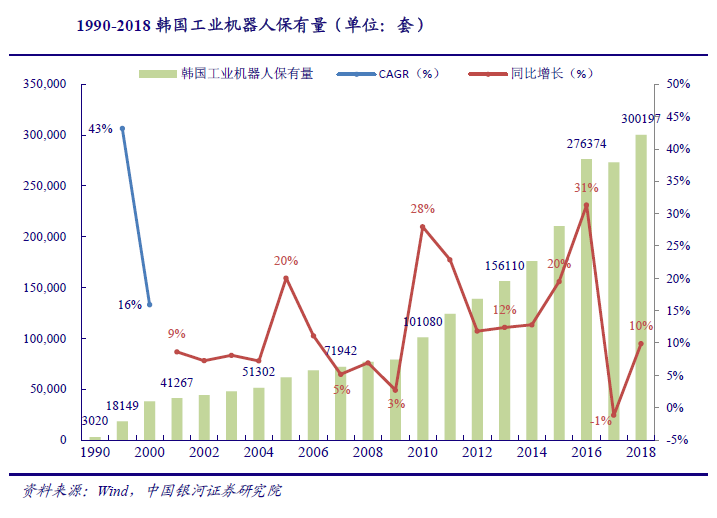
Natural driving factors such as the change of early population structure and the increase of labor cost will generally promote the natural transition from "human" to "robot". However, after the basic settlement of prominent problems such as labor force, the growth rate of industrial robot ownership in South Korea surged from 2.7% to 28% in 2010. At this stage, South Koreas outstanding demand for robots mainly stems from the countrys industrial characteristics, That is, South Koreas developed automobile and 3C industries.
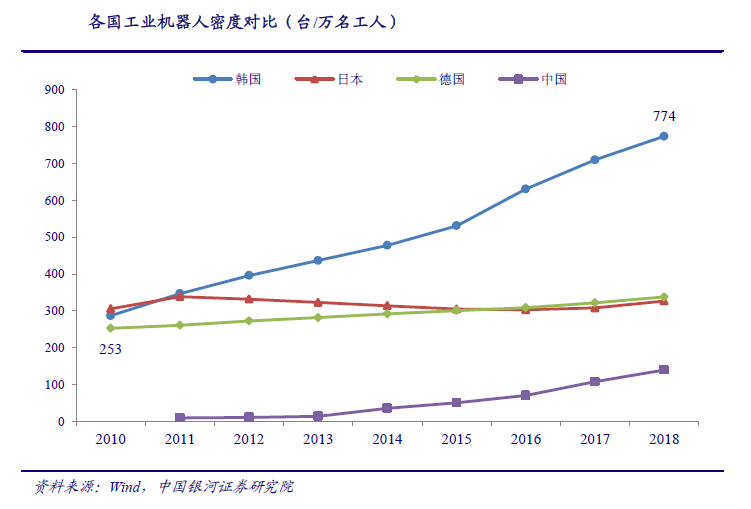
South Korea has the highest density of robots deployed, far exceeding the global average. Globally, South Korea is currently the country with the highest density of robots deployed in the manufacturing industry. The robot density in South Korea (774 sets / 10000 workers) is about 7 times higher than the global average (99 sets / 10000 workers) and 1.3 times higher than that in Germany with developed manufacturing industry (338 sets / 10000 workers), It is still 1.4 times higher than Japan (327 sets / 10000 workers), which developed earlier than industrial robots. The reason for the high density of industrial robots in Korea is inseparable from the attributes of its downstream application industry.

(2) Downstream applications of industrial robots: the automobile industry accounts for the largest proportion and 3C industry grows the fastest
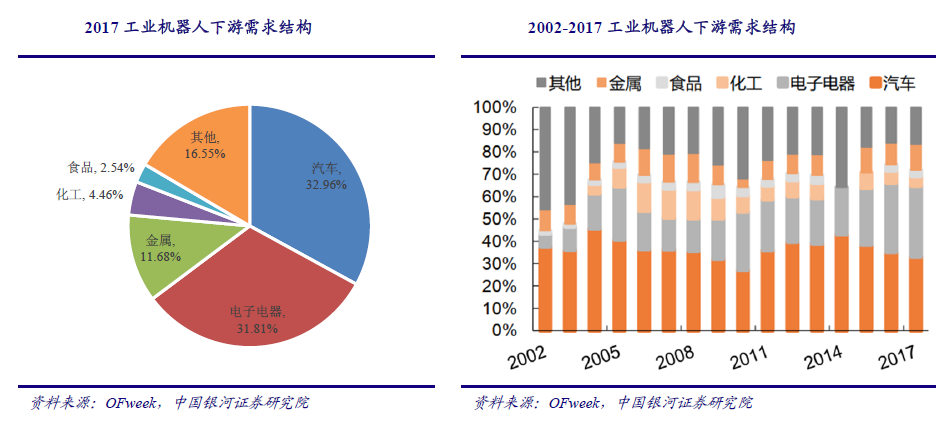
Originally, the birth of industrial robots was to alleviate the shortage of young labor force and engage in some repetitive and high-intensity manual labor. In recent years, with the continuous rise of the total installed capacity in emerging markets, the application fields of industrial robots have been gradually expanded. The industries with more applications mainly include automobile, electronics and electrical appliances, metal products, chemical industry, food manufacturing and other industries. In 2017, the global application proportion of industrial robots in the above industries was 32.96%, 31.81%, 11.68%, 4.46% and 2.54% respectively. Looking back over the past decade, the application of industrial robots in the electronic and electrical industry has grown the fastest. In 2002, the application proportion of industrial robots in this field was only 1.06%, and in 2017, it has increased to 31.81%.
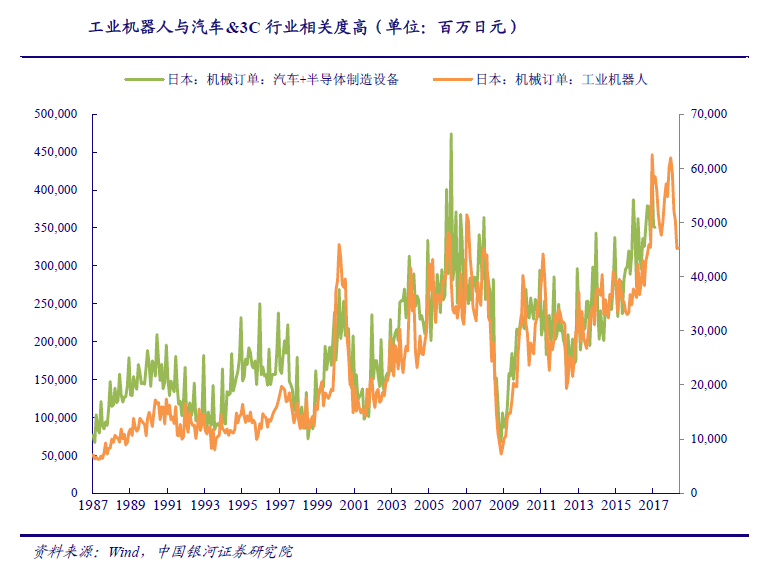
Downstream demand for industrial robots is concentrated in cars & amp; 3C, the orders of the two industries are highly correlated with the orders of industrial robots. Comparing the data of Japanese automobile and semiconductor manufacturing with the orders of Japanese industrial robots, it is found that the trend of these two groups of data is relatively consistent, and the correlation coefficient is close to 0.8, which also confirms that the main downstream of the industrial robot market is concentrated in the automobile and 3C electronics industries. Although the downstream application distribution of industrial robots in various countries is different, the order volume of automotive and electronic industries can be used as the leading index of industrial robots to a certain extent.
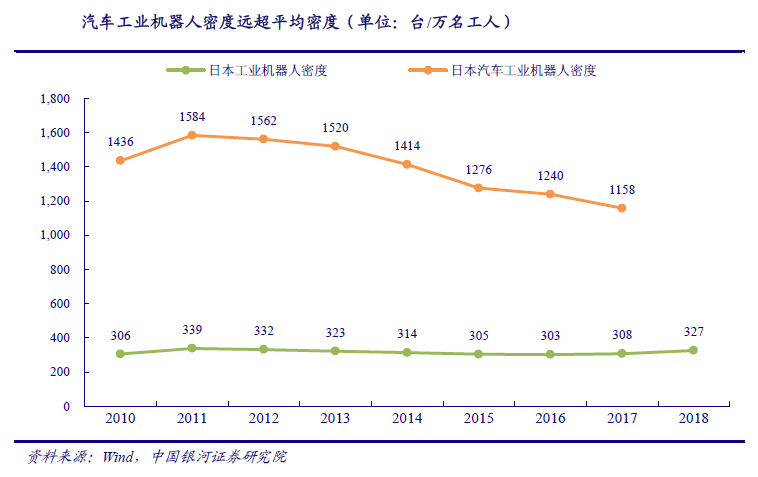
According to Japanese data, the density of industrial robots in the automobile industry is far higher than the average density of industrial robots. The technical level and automation degree of modern automobile production line are constantly improving, and more and more robot applications are constantly developed to replace traditional manpower. Therefore, industrial robots are widely used in various production links of automobile, and the automobile industry is the field with the highest automation rate of industrial robots. The density of robots in Japans automobile industry has long exceeded the average density of industrial robots. In 2017, the density of industrial robots in Japan was 308 sets / 10000 workers, while the density of robots in the automobile industry was 1158 sets / 10000 workers.
(3) South Koreas automobile and 3C industries highlight the demand and bring high industrial robot density
Car & amp; As a pillar industry in South Korea, 3C industry has spawned a huge demand for industrial robots. South Koreas auto industry started in the middle and late 1950s. From 1962 to 1990, the South Korean government promoted the development of the auto industry by setting up various tariff and non-tariff barriers to restrict foreign auto imports, actively attracting foreign advanced auto parts enterprises to build factories in South Korea, and developing new models with high scientific and technological content. In the early stage of the development of 3C industry in South Korea, gradual steps such as learning imitation and design innovation were taken to cultivate several large furniture enterprises with international competitiveness. In the later stage, South Koreas 3C industry strengthened R & D and technological innovation. In 1992, South Koreas electronic industry invested $1.557 billion in R & D, accounting for 4.44% of the turnover. It gradually gained world popularity, and its export increased day by day, forming an automobile & amp; Outstanding situation of 3C industry. From 2005 to 2015, the automobile output ranked fifth in the world for 11 consecutive years, creating well-known Korean car enterprises such as Hyundai, Kia, Renault and Samsung. 3C industry is also one of the pillar industries in South Korea. In 2018, the output of South Koreas electronics industry was US $171.101 billion, ranking third in the world, behind China and the United States and surpassing Japan. Car & amp; The contribution rate of 3C industry output value to GDP is 20.81%, and that of China, Japan and the United States are 14.10%, 13.30% and 3.3% respectivelyCompared with other countries, South Koreas automobile and 3C industries are more important.

Downstream demand for industrial robots is mainly concentrated in Automobiles & amp; 3C and other labor-intensive industries, so the automobile and 3C industries, as the two pillar enterprises in South Korea, have effectively promoted the development of the third stage of industrial robots in South Korea. In 2010, the density of industrial robots in South Korea was 287 sets / 10000 workers, and rapidly increased to 774 sets / 10000 workers in 2018, with CAGR as high as 13. 20%, becoming the country with the highest density of industrial robots in the world.
Through the analysis of the development process of industrial robots in Japan, Germany and South Korea, it can be seen that the change of population structure and the surge of labor cost are often the natural driving force for the early development of industrial robots in various countries. When the prominent contradiction of labor force is basically solved, the growth rate of industrial robot ownership in a country will generally tend to be flat. At this time, the industrial characteristics of various countries (such as whether they have developed downstream application industries) have become the differentiation point of industrial robot demand in different countries, and also constitute the secondary driving force of industrial robot growth.
(1) South Korea has the highest density of robots deployed, far exceeding the global average
Natural driving factors such as the change of early population structure and the increase of labor cost will generally promote the natural transition from "human" to "robot". However, after the basic settlement of prominent problems such as labor force, the growth rate of industrial robot ownership in South Korea surged from 2.7% to 28% in 2010. At this stage, South Koreas outstanding demand for robots mainly stems from the countrys industrial characteristics, That is, South Koreas developed automobile and 3C industries.


South Korea has the highest density of robots deployed, far exceeding the global average. Globally, South Korea is currently the country with the highest density of robots deployed in the manufacturing industry. The robot density in South Korea (774 sets / 10000 workers) is about 7 times higher than the global average (99 sets / 10000 workers) and 1.3 times higher than that in Germany with developed manufacturing industry (338 sets / 10000 workers), It is still 1.4 times higher than Japan (327 sets / 10000 workers), which developed earlier than industrial robots. The reason for the high density of industrial robots in Korea is inseparable from the attributes of its downstream application industry.

(2) Downstream applications of industrial robots: the automobile industry accounts for the largest proportion and 3C industry grows the fastest
Originally, the birth of industrial robots was to alleviate the shortage of young labor force and engage in some repetitive and high-intensity manual labor. In recent years, with the continuous rise of the total installed capacity in emerging markets, the application fields of industrial robots have been gradually expanded. The industries with more applications mainly include automobile, electronics and electrical appliances, metal products, chemical industry, food manufacturing and other industries. In 2017, the global application proportion of industrial robots in the above industries was 32.96%, 31.81%, 11.68%, 4.46% and 2.54% respectively. Looking back over the past decade, the application of industrial robots in the electronic and electrical industry has grown the fastest. In 2002, the application proportion of industrial robots in this field was only 1.06%, and in 2017, it has increased to 31.81%.

Downstream demand for industrial robots is concentrated in cars & amp; 3C, the orders of the two industries are highly correlated with the orders of industrial robots. Comparing the data of Japanese automobile and semiconductor manufacturing with the orders of Japanese industrial robots, it is found that the trend of these two groups of data is relatively consistent, and the correlation coefficient is close to 0.8, which also confirms that the main downstream of the industrial robot market is concentrated in the automobile and 3C electronics industries. Although the downstream application distribution of industrial robots in various countries is different, the order volume of automotive and electronic industries can be used as the leading index of industrial robots to a certain extent.

According to Japanese data, the density of industrial robots in the automobile industry is far higher than the average density of industrial robots. The technical level and automation degree of modern automobile production line are constantly improving, and more and more robot applications are constantly developed to replace traditional manpower. Therefore, industrial robots are widely used in various production links of automobile, and the automobile industry is the field with the highest automation rate of industrial robots. The density of robots in Japans automobile industry has long exceeded the average density of industrial robots. In 2017, the density of industrial robots in Japan was 308 sets / 10000 workers, while the density of robots in the automobile industry was 1158 sets / 10000 workers.

(3) South Koreas automobile and 3C industries highlight the demand and bring high industrial robot density
Car & amp; As a pillar industry in South Korea, 3C industry has spawned a huge demand for industrial robots. South Koreas auto industry started in the middle and late 1950s. From 1962 to 1990, the South Korean government promoted the development of the auto industry by setting up various tariff and non-tariff barriers to restrict foreign auto imports, actively attracting foreign advanced auto parts enterprises to build factories in South Korea, and developing new models with high scientific and technological content. In the early stage of the development of 3C industry in South Korea, gradual steps such as learning imitation and design innovation were taken to cultivate several large furniture enterprises with international competitiveness. In the later stage, South Koreas 3C industry strengthened R & D and technological innovation. In 1992, South Koreas electronic industry invested $1.557 billion in R & D, accounting for 4.44% of the turnover. It gradually gained world popularity, and its export increased day by day, forming an automobile & amp; Outstanding situation of 3C industry. From 2005 to 2015, the automobile output ranked fifth in the world for 11 consecutive years, creating well-known Korean car enterprises such as Hyundai, Kia, Renault and Samsung. 3C industry is also one of the pillar industries in South Korea. In 2018, the output of South Koreas electronics industry was US $171.101 billion, ranking third in the world, behind China and the United States and surpassing Japan. Car & amp; The contribution rate of 3C industry output value to GDP is 20.81%, and that of China, Japan and the United States are 14.10%, 13.30% and 3.3% respectivelyCompared with other countries, South Koreas automobile and 3C industries are more important.

Downstream demand for industrial robots is mainly concentrated in Automobiles & amp; 3C and other labor-intensive industries, so the automobile and 3C industries, as the two pillar enterprises in South Korea, have effectively promoted the development of the third stage of industrial robots in South Korea. In 2010, the density of industrial robots in South Korea was 287 sets / 10000 workers, and rapidly increased to 774 sets / 10000 workers in 2018, with CAGR as high as 13. 20%, becoming the country with the highest density of industrial robots in the world.
Through the analysis of the development process of industrial robots in Japan, Germany and South Korea, it can be seen that the change of population structure and the surge of labor cost are often the natural driving force for the early development of industrial robots in various countries. When the prominent contradiction of labor force is basically solved, the growth rate of industrial robot ownership in a country will generally tend to be flat. At this time, the industrial characteristics of various countries (such as whether they have developed downstream application industries) have become the differentiation point of industrial robot demand in different countries, and also constitute the secondary driving force of industrial robot growth.

