Fan Cheng Bionic black Technology: jellyfish robot capable of military surveillance and underwat
Published on:2020-04-23
Bionic robots have made new breakthroughs and progress in recent years. Before that, FESTOs "bionic Dragonfly" amazed everyone, and then various types of bionic underwater robots emerged in endlessly. Most bionic underwater robots are made by simulating the swimming principle of tuna, carp and other fish. However, this kind of bionic robot can rarely swim in the vertical direction.

In recent years, jellyfish with its efficient and flexible jet propulsion has gradually become the object of biomimetic scientists. Recently, Yonas Tadesse, a researcher at the University of Texas at Dallas, developed a bionic jellyfish soft robot that can swim vertically and has a certain load.
The movement mechanism of the bionic jellyfish soft robot is to generate reaction force by spraying fluid downward to promote its vertical movement in the water environment.

Bionic jellyfish soft robot
The researchers equipped the robot with eight latest inflatable flexible pneumatic composite actuators arranged radially, and powered by an air compressor. The composite actuator consists of a single chamber and a thin spring steel sheet on the outer layer. The main material of the chamber is organic silica gel resin. The outer spring steel is a non stretchable material, but it has good rebound effect. When a force acts on one end of the steel sheet and is suddenly released, the steel sheet can quickly retract to its original position.
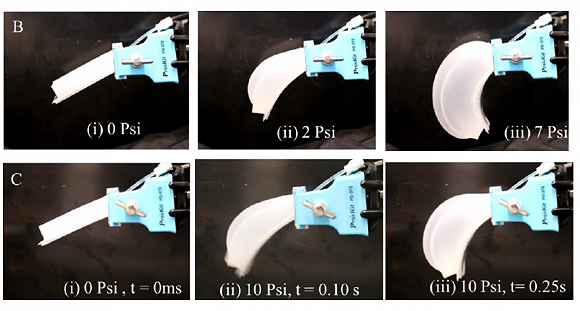
Inflatable flexible pneumatic composite actuator. Source: University of Texas
The researchers designed the composite actuator with thick side and thin top to maximize the air entering the chamber. By injecting air into the compressor, the actuator can expand and bend rapidly, generate large instantaneous thrust and realize rapid movement in the vertical direction. After testing, the bionic jellyfish soft robot with a diameter of 220 mm can bear a load of 100 grams in the fish tank and swim vertically at a speed of 16 cm / s.
Jonas said that compared with the previous bionic jellyfish robot, this robot has the fastest vertical rise speed.
In addition to military surveillance, the robot can also be used in underwater rapid rescue, seabed exploration, resource exploration, underwater terrain survey and other aspects in the future. Compared with traditional rigid robots, soft robots are generally made of flexible materials with great variability, which can realize large-scale continuous deformation and arbitrarily change their size and shape. Therefore, soft robot is also regarded as the future of robot technology in the industry.
Previously, scientists have taken a lot of inspiration from jellyfish.
According to the world wide web, in July last year, the British Journal natural Communication published a new study. Metin sitti of the Max Planck Institute for intelligent systems in Germany and his colleagues invented a soft robot inspired by the saucer larvae of bowl jellyfish.

A soft robot inspired by the saucer larvae of bowl jellyfish. Source: nature Newsletter
The soft robot has a total length of 6 mm and 8 arms and feet. Its tip is made of non-magnetic polymer and its whole body is embedded with magnetic particles. The researchers put the robot in the water tank and put an electromagnetic coil around the outside of the water tank. As long as you manipulate the magnetic field, you can wirelessly control its wrists and feet to contract and recover, just like a swimming jellyfish. This cableless soft robot is small, but it has the functions of transportation, drilling and so on.
In January, researchers at the California Institute of technology and Stanford University also invented a miniature electronic semi robot jellyfish, according to advanced science news.
John Dabiri, a professor at Stanford University, who is in charge of the research team, said that now a lot of research has turned to the development of bionic robots that simulate organisms, but equipping organisms with electronic components is also a new way of bionic robot research.
Miniature electronic semi robot jellyfish. Source: Stanford University
Researchers at Stanford University have equipped jellyfish with a microelectronic controller that can emit electrical pulses, just like installing a pacemaker. After testing, the jellyfish equipped with microelectronic controller has a pulse frequency three times that of ordinary jellyfish. This increases the swimming speed of jellyfish from 2 cm / s to 4-6 cm / s.
Stanford researchers said the research is still in its infancy and hope to develop a sufficiently small electronic device embedded in jellyfish tissue in the future. In addition to controlling its swimming speed, it can also control its movement direction, which can be applied to ocean exploration.

In recent years, jellyfish with its efficient and flexible jet propulsion has gradually become the object of biomimetic scientists. Recently, Yonas Tadesse, a researcher at the University of Texas at Dallas, developed a bionic jellyfish soft robot that can swim vertically and has a certain load.
The movement mechanism of the bionic jellyfish soft robot is to generate reaction force by spraying fluid downward to promote its vertical movement in the water environment.

Bionic jellyfish soft robot
The researchers equipped the robot with eight latest inflatable flexible pneumatic composite actuators arranged radially, and powered by an air compressor. The composite actuator consists of a single chamber and a thin spring steel sheet on the outer layer. The main material of the chamber is organic silica gel resin. The outer spring steel is a non stretchable material, but it has good rebound effect. When a force acts on one end of the steel sheet and is suddenly released, the steel sheet can quickly retract to its original position.

Inflatable flexible pneumatic composite actuator. Source: University of Texas
The researchers designed the composite actuator with thick side and thin top to maximize the air entering the chamber. By injecting air into the compressor, the actuator can expand and bend rapidly, generate large instantaneous thrust and realize rapid movement in the vertical direction. After testing, the bionic jellyfish soft robot with a diameter of 220 mm can bear a load of 100 grams in the fish tank and swim vertically at a speed of 16 cm / s.
Jonas said that compared with the previous bionic jellyfish robot, this robot has the fastest vertical rise speed.
In addition to military surveillance, the robot can also be used in underwater rapid rescue, seabed exploration, resource exploration, underwater terrain survey and other aspects in the future. Compared with traditional rigid robots, soft robots are generally made of flexible materials with great variability, which can realize large-scale continuous deformation and arbitrarily change their size and shape. Therefore, soft robot is also regarded as the future of robot technology in the industry.
Previously, scientists have taken a lot of inspiration from jellyfish.
According to the world wide web, in July last year, the British Journal natural Communication published a new study. Metin sitti of the Max Planck Institute for intelligent systems in Germany and his colleagues invented a soft robot inspired by the saucer larvae of bowl jellyfish.

A soft robot inspired by the saucer larvae of bowl jellyfish. Source: nature Newsletter
The soft robot has a total length of 6 mm and 8 arms and feet. Its tip is made of non-magnetic polymer and its whole body is embedded with magnetic particles. The researchers put the robot in the water tank and put an electromagnetic coil around the outside of the water tank. As long as you manipulate the magnetic field, you can wirelessly control its wrists and feet to contract and recover, just like a swimming jellyfish. This cableless soft robot is small, but it has the functions of transportation, drilling and so on.
In January, researchers at the California Institute of technology and Stanford University also invented a miniature electronic semi robot jellyfish, according to advanced science news.
John Dabiri, a professor at Stanford University, who is in charge of the research team, said that now a lot of research has turned to the development of bionic robots that simulate organisms, but equipping organisms with electronic components is also a new way of bionic robot research.

Miniature electronic semi robot jellyfish. Source: Stanford University
Researchers at Stanford University have equipped jellyfish with a microelectronic controller that can emit electrical pulses, just like installing a pacemaker. After testing, the jellyfish equipped with microelectronic controller has a pulse frequency three times that of ordinary jellyfish. This increases the swimming speed of jellyfish from 2 cm / s to 4-6 cm / s.
Stanford researchers said the research is still in its infancy and hope to develop a sufficiently small electronic device embedded in jellyfish tissue in the future. In addition to controlling its swimming speed, it can also control its movement direction, which can be applied to ocean exploration.

